What Is Insulin Resistance? Symptoms, Causes & Diet
What Is Insulin Resistance? Symptoms, Causes & Diet
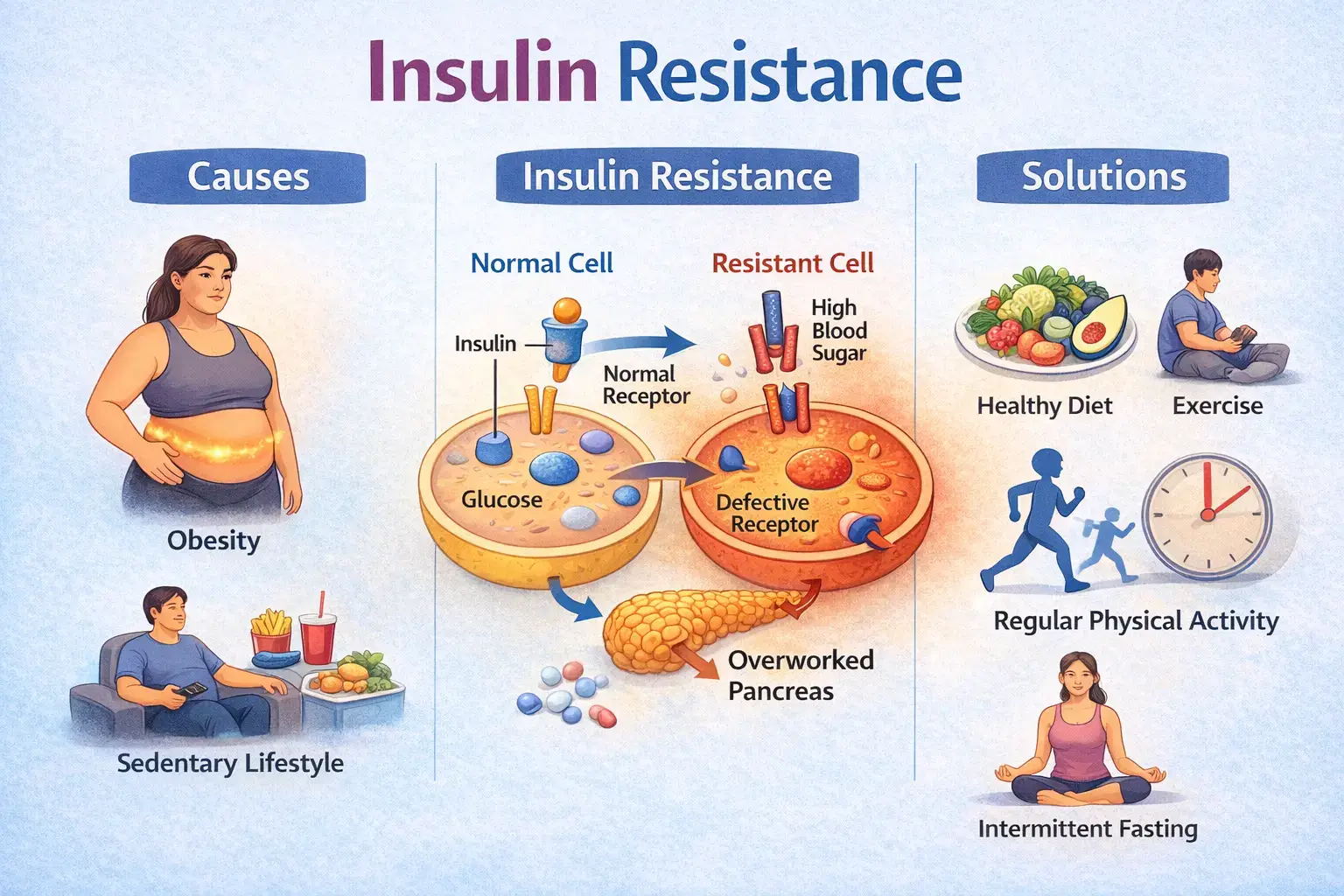
Insulin resistance is a metabolic condition in which the body’s cells do not respond effectively to insulin, a hormone responsible for regulating blood sugar levels. As a result, glucose remains in the bloodstream instead of being used efficiently for energy.
Insulin resistance does not exist in isolation. It is closely linked with other key aspects of women’s health such as hormonal imbalance, PCOS, thyroid dysfunction, micronutrient deficiencies, and chronic inflammation. To understand how insulin resistance fits into the broader picture, read our comprehensive guide on Women’s Health Explained: 6 Core Factors That Influence Hormones, Metabolism & Long-Term Health.
What Is Insulin Resistance?
Insulin acts like a key that allows glucose to enter your cells. When cells become resistant to insulin, this “key” does not work efficiently. The pancreas compensates by producing more insulin to maintain normal blood sugar levels. Over time, this increased demand can strain the pancreas and raise the risk of prediabetes and type 2 diabetes.
Symptoms of Insulin Resistance
- Increased waist circumference or abdominal fat
- Persistent fatigue or low energy levels
- Strong cravings for sugar or refined carbohydrates
- Difficulty losing weight despite calorie control
- Elevated triglycerides or low HDL cholesterol
Low energy in insulin resistance is not always driven by blood sugar imbalance alone. Iron deficiency and low ferritin levels can further reduce stamina and worsen fatigue. Learn more about iron deficiency as a hidden cause of chronic fatigue in women .
In many individuals, insulin resistance develops silently and may not cause obvious symptoms in the early stages. This is why regular metabolic screening is important.
Causes of Insulin Resistance
Insulin resistance develops due to a combination of lifestyle, metabolic, and genetic factors. Common contributors include:
- Excess body fat, especially around the abdomen
- Low levels of physical activity
- Diets high in refined carbohydrates and added sugars
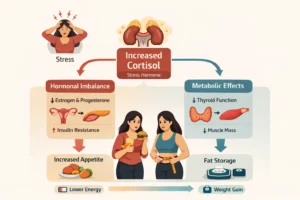
- Poor sleep quality and chronic stress
- Hormonal conditions such as PCOS
In addition to lifestyle factors, genetic variations can influence insulin sensitivity. Genes such as INSR and TCF7L2 are known to affect insulin signalling and glucose metabolism. These differences may explain why some individuals develop insulin resistance more easily than others, even when following similar diets or activity levels.
Diet and Lifestyle to Improve Insulin Sensitivity
Improving insulin sensitivity requires a consistent and balanced approach rather than extreme dietary restriction.
- Prioritise whole foods such as vegetables, fruits, whole grains, and lean protein
- Reduce intake of refined sugars, processed foods, and sugary beverages
- Include regular physical activity, combining strength training and aerobic exercise
- Maintain regular meal timings to avoid blood sugar spikes
- Focus on adequate sleep and stress management
Strength training improves muscle glucose uptake, while aerobic activity supports overall metabolic flexibility. Both forms of movement play a role in improving insulin sensitivity.
How Insulin Resistance Connects to Other Women’s Health Factors
Insulin resistance often overlaps with other health concerns rather than occurring alone. It is commonly associated with thyroid dysfunction, micronutrient deficiencies such as vitamin D deficiency, and chronic low-grade inflammation.
Addressing insulin resistance alongside these factors leads to better long-term outcomes compared to focusing on blood sugar alone.
Related Guides
- PCOS Diet Plan: Foods to Eat and Avoid
- Vitamin D Deficiency: Symptoms, Causes & Diet
- Hypothyroidism and Nutrition
- 11 Blood Tests That Reveal Metabolic Health
- DNA-Based Diet for Weight Loss for Indian Women
Frequently Asked Questions
Can insulin resistance be reversed?
In many cases, insulin resistance can be improved or reversed through consistent dietary changes, physical activity, stress management, and weight optimisation.
Does meal timing matter for insulin resistance?
Yes. Regular meal timings and balanced meals help stabilise blood sugar levels and reduce metabolic stress.
Is insulin resistance only related to weight?
No. Insulin resistance can occur even in individuals with normal body weight, especially when muscle mass is low or hormonal imbalance is present.
Final Takeaway
Insulin resistance is a key metabolic issue that influences weight, energy levels, and hormonal health, especially in women. While lifestyle factors play a major role, genetic differences, hormonal balance, nutrient status, and thyroid health also contribute to how the body responds to insulin.
Insulin resistance plays a central role in women’s metabolic and hormonal health and often overlaps with conditions such as PCOS, thyroid imbalance, and nutrient deficiencies.
To see how insulin resistance connects with other core aspects of women’s health, read our detailed framework here: Women’s Health Explained: 6 Core Factors That Influence Hormones, Metabolism & Long-Term Health .
If you are experiencing unexplained fatigue, weight gain, or difficulty managing blood sugar, a personalised approach that considers blood tests, lifestyle, and individual biology can help identify root causes.
👉 Book a FREE consultation with our clinical nutrition team to understand your metabolic profile and receive personalised nutrition guidance tailored to your body.
Book Your Free Consultation
Share this article
Nihala Ibrahim
Nihala Ibrahim is a clinical dietitian with a scientific approach to personalized nutrition and metabolic health. She passionately bridges clinical insights with evidence-based diet strategies to help clients overcome diabetes, thyroid issues, PCOS, and weight challenges for optimal wellness. She holds Masters in clinical dietetics and nutrition science from Sri Ramachandra Institute, Chennai.