Protein Rich Foods for Vegetarians (Indian Diet Guide)

Getting enough protein on a vegetarian diet is a common concern in India. The good news is that Indian vegetarian diets can easily meet protein needs when planned correctly.
This guide explains the best protein rich foods for vegetarians, especially suitable for Indian households.
Why Protein Is Important
Protein helps:
Maintain muscle mass
Improve metabolism
Control hunger and cravings
Support blood sugar control
For adults, protein intake becomes even more important after the age of 35.
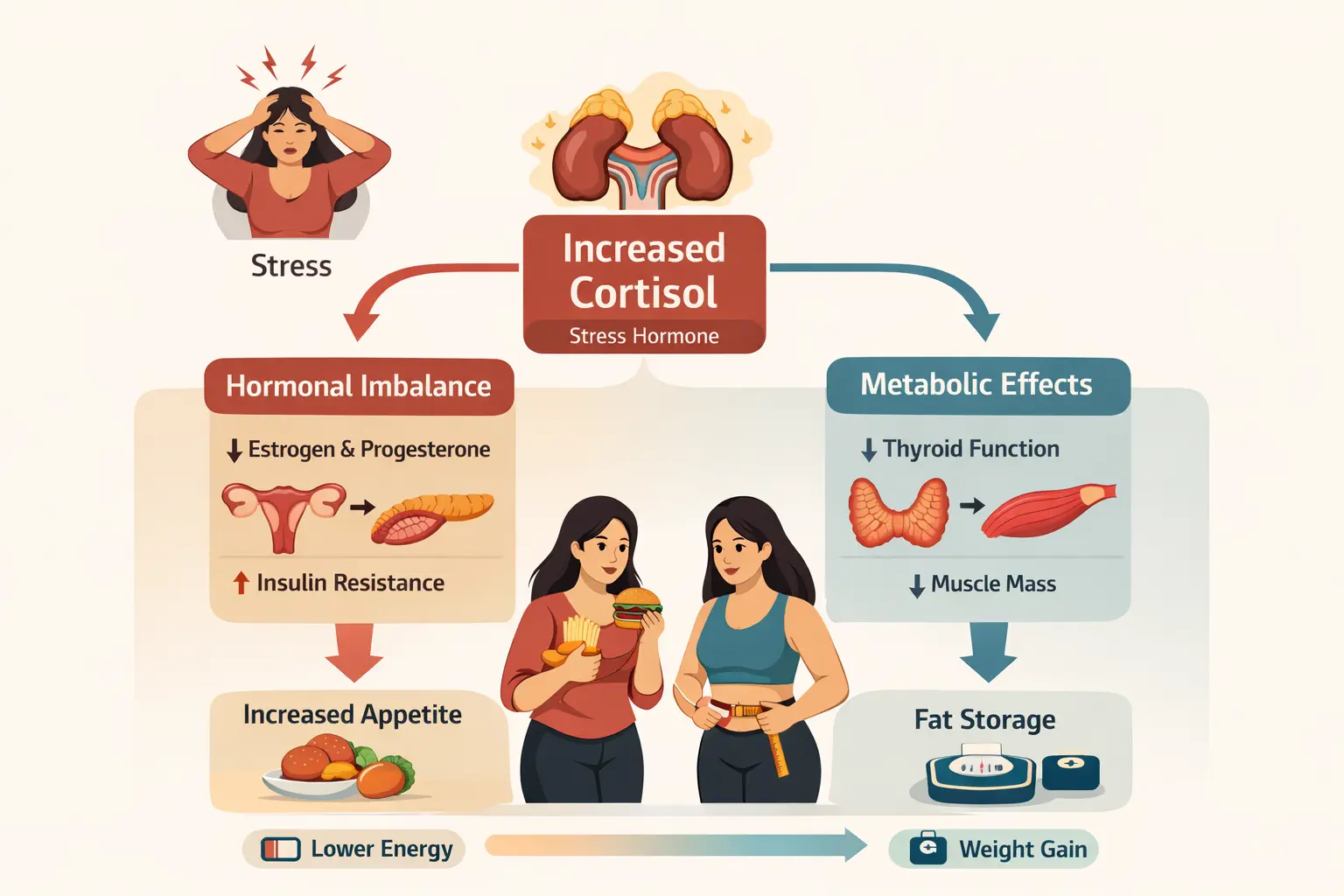
Maintaining stable blood sugar levels is especially important for women with metabolic conditions such as insulin resistance. Adequate protein intake helps slow glucose absorption, reduce insulin spikes, and support better metabolic balance.
To understand how blood sugar regulation and metabolism are affected at a deeper level, read our detailed guide on Insulin Resistance, its symptoms, causes, and dietary management.
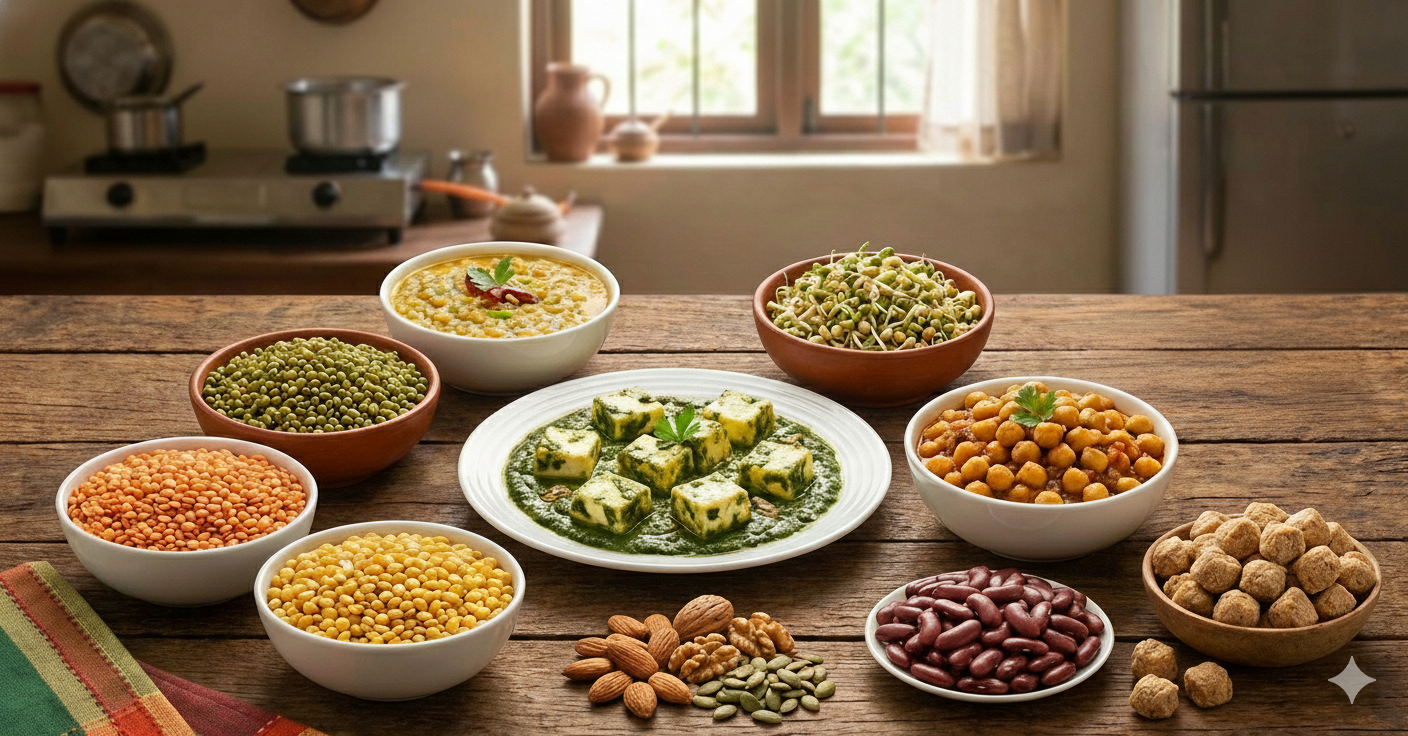
High Protein Foods for Vegetarians in India
1. Paneer and Curd
Paneer is rich in protein and calcium
Greek-style curd provides high-quality protein
Best consumed in controlled portions.
2. Dal, Lentils, and Pulses
Moong dal
Masoor dal
Chana
Rajma
Combining dal with grains improves protein quality.
3. Soya and Tofu
Tofu
Soy chunks
Edamame
Among the highest protein vegetarian foods available.
4. Whole Grains
Quinoa
Millets (ragi, jowar, bajra)
Oats
These add protein along with complex carbohydrates.
Common Mistakes in Vegetarian Protein Intake
Relying only on dal
Skipping protein at breakfast
Avoiding fats completely
Overusing protein supplements
Balanced meals work better than supplements for most people.
How to Distribute Protein Across the Day (Often Overlooked)
One of the most important but overlooked aspects of vegetarian protein intake is distribution across meals. Many people consume very little protein at breakfast, moderate amounts at lunch, and most of it at dinner. This uneven pattern reduces protein utilization and muscle maintenance, especially after the age of 35. Ideally, protein should be spread evenly across the day—at breakfast, lunch, dinner, and even snacks. Simple changes such as adding curd, paneer, tofu, sprouts, or nuts to breakfast, including dal or legumes in lunch, and balancing dinner with adequate protein can significantly improve overall protein intake without increasing calories
Can Vegetarians Meet Protein Needs Without Supplements?
Yes. Most people can meet their protein requirements through whole foods, provided meals are well planned.
Supplements may be useful only in specific cases such as intense training or medical conditions.
Personalized Protein Needs
Protein requirements vary based on:
Age
Activity level
Weight goals
Blood markers
A personalized plan ensures you get enough protein without excess calories.
This is why a personalized nutrition plan based on your unique DNA & blood reports delivers better and more sustainable results than a generic diet chart.
| Food Item | Serving Size | Protein (g) | Calories (kcal) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Paneer (regular) | 100 g | 18–20 | ~265 | High protein, calorie-dense; portion control needed |
| Low-fat Paneer | 100 g | 20–22 | ~150 | Better for weight management |
| Curd (thick) | 1 cup (200 g) | 8–10 | ~120 | Easy to digest, probiotic benefits |
| Greek-style curd | 200 g | 15–18 | ~150 | Higher protein than regular curd |
| Moong Dal (cooked) | 1 cup | 14–15 | ~210 | Easy digestion, good amino acid profile |
| Masoor Dal (cooked) | 1 cup | 17–18 | ~230 | Iron-rich, good protein density |
| Rajma (cooked) | 1 cup | 15–16 | ~240 | High fiber, slow digestion |
| Chickpeas (Chana) | 1 cup | 14–15 | ~260 | Good satiety, moderate calories |
| Tofu | 100 g | 12–14 | ~120 | Low calorie, versatile protein |
| Soy Chunks (dry) | 50 g | 25–26 | ~170 | Very high protein; limit to 3–4×/week |
| Edamame (boiled) | 1 cup | 17–18 | ~190 | Complete plant protein |
| Quinoa (cooked) | 1 cup | 8 | ~220 | Better amino acid profile than rice |
| Oats (dry) | 40 g | 5–6 | ~150 | Good for breakfast, not a primary protein source |
| Millets (ragi, jowar, bajra) | 1 cup (cooked) | 6–7 | ~190 | Good minerals, moderate protein |
| Mixed Nuts | 30 g | 5–6 | ~170 | Protein + fats; calorie dense |
| Seeds (pumpkin/sunflower) | 30 g | 7–9 | ~160 | Good add-on, not a primary protein source |
Get A Free Consultation
If you want a diet plan tailored to needs, lifestyle, and food preferences, you can start with a free expert consultation.
Share this article
Nupur Sharma
Nupur Sharma is a Sports Nutritionist. She has a scientific approach towards nutrition. She passionately unfolds latent aspects linking nutritional science and sports performance so that athletes and fitness enthusiasts can achieve their highest potential. She holds a Master’s degree in Sports Nutrition and Bachelor’s degree in Food, Nutrition and Dietetics.